With so many AI models available today, the challenge is no longer about having access to a powerful model—it’s about choosing the right model for the right task. Imagine this – if you are paying for the top tier subscription of ChatGPT, currently you might get as many as 8 options in the model selection dropdown:
-> GPT-4o
-> GPT – 4o with scheduled tasks (in beta)
-> o1
-> o3-mini
-> o3 – mini – high
-> o1 pro mode
->GPT -4o mini
-> GPT -4
Even with a short description below the model name about what they are best suited for, it becomes a distraction for someone when they land on the homepage and to keep selecting the best model for the task.
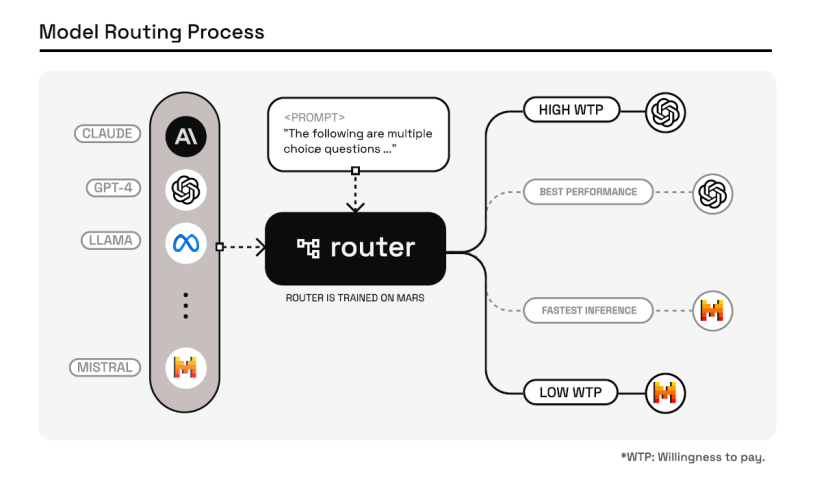
👉 This is where LLM routing becomes a key component in the AI architecture
Instead of using one AI model for everything, LLM routers act like traffic controllers, deciding which model should handle a given task. This makes AI systems faster, cheaper, and more efficient.
👉 How does it work?
There are two main ways LLM routing is done:
💠 Predictive routing – The router decides upfront which model is best for a query based on complexity, cost, and accuracy.
💠 Non-predictive routing – The router asks multiple models to generate responses first, then picks the best one.
💡 Think of it like choosing the right tool for a job. You don’t need a supercomputer to calculate 2+2, just like you don’t need GPT-4o or a o1 to check tomorrow’s weather.
Implementing a LLM router in your AI infrastructure can bring many benefits:
1️⃣ Saves cost – If a lightweight model can do the job, why use an expensive one?
2️⃣ Speeds up response time – Simple queries go to faster models, freeing up high-end models for tougher problems.
3️⃣ Improves accuracy – The router ensures the most suitable model answers each question.
👉 And what I am really excited about is, how in the future Routing Beyond LLMs
Right now, routing is mostly used for language models (LLMs), but in the future, it could route between different AI models (LAM, LCM etc.) based on the type of task:
💠 If a task requires reasoning → The router picks an Large concept model.
💠 If a task involves action (e.g., booking a flight) → The router picks an Large Action Model.
💠 If a task requires long-term memory → The router picks an Large Context Model.
I strongly believe that LLM Routers or in future we call them AI routers will play a vital role in an AI ecosystem where multiple model types work together seamlessly.
Read the below 2 papers for more details:
-> https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.12031
-> https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.18665