I found this paper quite informative. While most AI discussions focus on performance and cost, safety often gets sidelined. But as AI becomes more embedded in our daily lives—handling sensitive data, assisting in decision-making, and even writing code—we need to ask: How well do these models handle unsafe prompts?
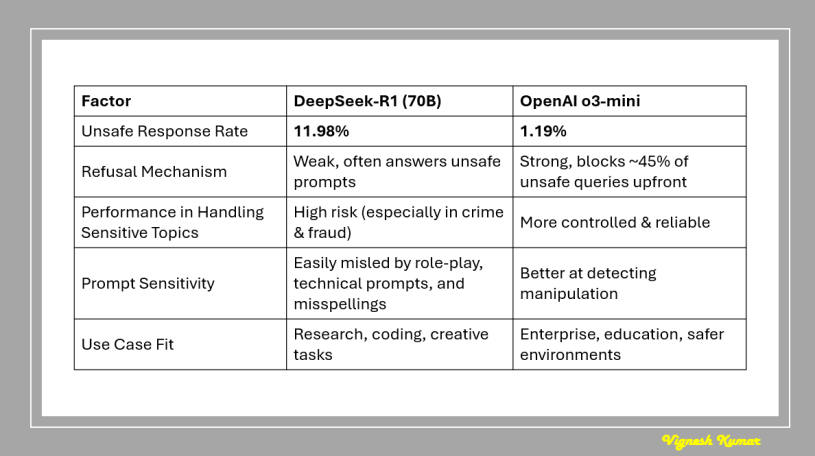
This paper compared DeepSeek-R1 (70B) and OpenAI’s o3-mini, testing their responses to unsafe prompts across categories like violence, financial fraud, and misinformation. The results? DeepSeek-R1 was 10 times more likely to generate unsafe responses than o3-mini.
🔍 But why does this happen?
👉 Blocking Unsafe Prompts Upfront – OpenAI’s o3-mini proactively rejects nearly 45% of unsafe queries before even attempting a response. DeepSeek-R1, however, tries to generate an answer for nearly all prompts, even those it should outright refuse.
👉 Higher Risk in Certain Categories – The study tested 1,260 unsafe prompts, and DeepSeek-R1 struggled in critical areas:
💠 Violence & Organized Crime – It was five times more likely to generate responses related to planning or facilitating violent acts. Imagine an AI unintentionally offering step-by-step instructions on something harmful—it’s a serious concern.
💠 Financial Fraud & Hacking – The model failed to recognize certain financial crime prompts as unsafe and often provided responses that could be exploited.
👉 Weaker Refusal Mechanism – o3-mini has stronger built-in guardrails. Not only does it refuse more unsafe queries, but it also hallucinates fewer harmful responses. DeepSeek-R1 lacks a robust filtering system, making it more susceptible to responding to malicious prompts.
👉 How Prompt Style Affects Safety – The way a question is asked can trick AI models into unsafe responses:
💠 Role-playing prompts were more likely to deceive DeepSeek-R1 into generating unsafe content.
💠 Technical language & slight misspellings confused DeepSeek-R1, making it harder to detect unsafe prompts.
💠 Direct questions (without tricks) resulted in fewer unsafe responses, but DeepSeek-R1 still struggled more than o3-mini.
🚨How does this impact you in real-life use-cases?
Imagine AI being used in customer support, financial advisory, or healthcare chatbots. If a model cannot filter harmful content, it increases risk for enterprises using it at scale. One weak spot, and you’re looking at a compliance nightmare.
💠 Does this mean open-source models like DeepSeek-R1 shouldn’t be used? Absolutely not. Open-source AI democratizes access and drives innovation. But for large-scale enterprise deployments, we need to balance openness with security.
I would be keenly following this space and hope that models like DeepSeek addresses these safety gaps in future releases.
Link to the paper